Catalysing the use of data and digital technology for tourism in Ghana
Catalysing the use of data and digital technology for tourism in Ghana
21 September, 2023 •Ghana’s tourism industry presents an exciting landscape for growth, offering significant potential for youth employment and entrepreneurship. However, an effective digital presence is a prerequisite for competitiveness in the global tourism sector and in Ghana, digital technology adoption among tourism operators remains nascent.
Data and digital technology increasingly enable tourism operators and related service providers (including public sector actors) to enhance their visibility, improve the tourist experience, and predict tourist activities. They also allow for the enhancement of their own service and product offerings through tools such as digital marketing, cashless payments, and the utilisation of data, such as customer feedback, for decision-making, respectively.
Tourists themselves are partially driving this trend. For instance, 82% of travellers are booking travel or tourist activities through a website or mobile app (Condor, 2023). In today’s global and digitalised tourism economy, tourist preferences and decisions are shaped by what they can see online.
To be globally competitive, Ghana’s rich physical and cultural tourism assets need to be complemented with an online presence that effectively conveys their desirability to tourists. It is not just that digital technology should be more widely adopted or that data be captured and effectively analysed, the digital tools and platforms adopted by tourism entities should account for the preferences of international tourists.
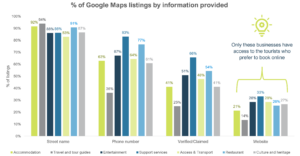
Sometimes there is a provider-user mismatch. Emails, for example, are often discarded in favour of WhatsApp in Ghana, and cash and mobile money are preferred to card payments and other digital payment options. Additionally, private and public sector stakeholders have not yet embraced a data and evidence-driven approach to decision-making. A key risk is that, without adapting, these institutions will lose market share, miss out on key insights that can provide a competitive edge and increase their cost of operations – ultimately preventing the tourism sector from reaching its full potential. Currently, the majority of Ghanaian tourism providers do not have an associated website presence linked to the Google Maps profile – as illustrated by the figure below.
To address these issues, Cenfri, in partnership with Mastercard Foundation and the Ghana Tourism Federation, has undertaken a project to support the development of Ghana’s tourism sector for job creation and growth by identifying and catalysing the enhanced use of data and digital technology. The project has two key objectives:
- To scope out existing challenges and opportunities within the Ghanaian tourism sector to inform a targeted approach for potential interventions that is based on known tourism drivers and outcomes derived from available data and other information sources.
- To convene, advocate and support relevant tourism value-chain actors to see the business case in sharing and better leveraging data sources held by actors for enhanced data-driven decision-making that can support initiatives aimed at job creation and revenue generation.
Read more about our other data-for-decision-making work here.
If you are interested in learning more about this project or in collaborating with us, please email Lezanne Anderson (lezanne@cenfri.org) or Jeremy Gray (jeremy@cenfri.org).